jueves, 3 de enero de 2013
The Sonic Barrier
Volver a Pagina Principal /Back to Mean Page / 首页 / Заглавная страница / मुखपृष्ठ / Hauptseite / Accueil / Recepção / Strona główna / الصفحة الرئيسية / メインページ / 대문 / หน้าหลัก / Huvudsida / Etusivu / Ana sayfa /עמודראשי
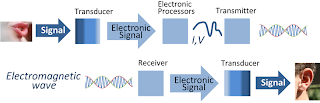
Transducer
A transducer is a device that converts one form of energy to another. Energy types include (but are not limited to) electrical, mechanical, electromagnetic (including light), chemical, acoustic or thermal energy. While the term transducer commonly implies the use of a sensor/detector, any device which converts energy can be considered a transducer. Transducers are widely used in measuring instruments.
A sensor is used to detect a parameter in one form and report it in another form of energy (usually an electrical and/or digital signal). For example, a pressure sensor might detect pressure (a mechanical form of energy) and convert it to electricity for display at a remote gauge.
An actuator accepts energy and produces movement (action). The energy supplied to an actuator might be electrical or mechanical (pneumatic, hydraulic, etc.). An electric motor and a loudspeaker are both actuators, converting electrical energy into motion for different purposes.
Combination transducers have both functions; they both detect and create action. For example, a typical ultrasonic transducer switches back and forth many times a second between acting as an actuator to produce ultrasonic waves, and acting as a sensor to detect ultrasonic waves. Rotating a DC electric motor's rotor will produce electricity and voice-coil speakers can also act as microphones.
Volver a Pagina Principal /Back to Mean Page / 首页 / Заглавная страница / मुखपृष्ठ / Hauptseite / Accueil / Recepção / Strona główna / الصفحة الرئيسية / メインページ / 대문 / หน้าหลัก / Huvudsida / Etusivu / Ana sayfa /עמודראשי
Transducer Applications
- Electromagnetic:
- Antenna – converts propagating electromagnetic waves to and from conducted electrical signals
- Magnetic cartridge – converts relative physical motion to and from electrical signals
- Tape head, Disk read-and-write head - converts magnetic fields on a magnetic medium to and from electrical signals
- Hall effect sensor – converts a magnetic field level into an electrical signal
- Electrochemical:
- Electromechanical (electromechanical output devices are generically called actuators):
- Electroactive polymers
- Galvanometer
- Microelectromechanical systems
- Rotary motor, linear motor
- Vibration powered generator
- Potentiometer when used for measuring position
- Linear variable differential transformer or Rotary variable differential transformer
- Load cell – converts force to mV/V electrical signal using strain gauge
- Accelerometer
- Strain gauge
- String potentiometer
- Air flow sensor
- Tactile sensor
- Electroacoustic:
- Loudspeaker, earphone – converts electrical signals into sound (amplified signal → magnetic field → motion → air pressure)
- Microphone – converts sound into an electrical signal (air pressure → motion of conductor/coil → magnetic field → electrical signal)
- Pickup (music technology) – converts motion of metal strings into an electrical signal (magnetism → electrical signal)
- Tactile transducer – converts electrical signal into vibration ( electrical signal → vibration)
- Piezoelectric crystal – converts deformations of solid-state crystals (vibrations) to and from electrical signals
- Geophone – converts a ground movement (displacement) into voltage (vibrations → motion of conductor/coil → magnetic field → signal)
- Gramophone pickup – (air pressure → motion → magnetic field → electrical signal)
- Hydrophone – converts changes in water pressure into an electrical signal
- Sonar transponder (water pressure → motion of conductor/coil → magnetic field → electrical signal)
- Ultrasonic transceiver, transmitting ultrasound (transduced from electricity) as well as receiving it after sound reflection from target objects, availing for imaging of those objects.
- Electro-optical (Photoelectric):
- Fluorescent lamp – converts electrical power into incoherent light
- Incandescent lamp – converts electrical power into incoherent light
- Light-Emitting Diode – converts electrical power into incoherent light
- Laser Diode – converts electrical power into coherent light
- Photodiode, photoresistor, phototransistor, photomultiplier – converts changing light levels into electrical signals
- Photodetector or photoresistor or light dependent resistor (LDR) – converts changes in light levels into changes in electrical resistance
- Cathode ray tube (CRT) – converts electrical signals into visual signals
- Electrostatic:
- Thermoelectric:
- Resistance temperature detector (RTD) - converts temperature into an electrical resistance signal
- Thermocouple - converts relative temperatures of metallic junctions to electrical voltage
- Peltier cooler
- Thermistor (includes PTC resistor and NTC resistor)
- Radioacoustic:
- Geiger–Müller tube – converts incident ionizing radiation to an electrical impulse signal
- Receiver (radio)
- transmitter-propagates electromagnetic transmissions to sound
Suscribirse a:
Comentarios (Atom)